The consensus algorithm is at the core of blockchain systems, ensuring consistency and reliability for the entire network. So what is it and how does it work?
To better understand this mechanism, AZCoin will help you delve into how nodes in the network reach consensus on the state of blockchain.
What is a consensus algorithm?
Consensus algorithm is a mechanism in distributed systems, especially in blockchains, to ensure that all members of the network agree on a common state of data.
The consensus algorithm solves the problem of reaching consensus or agreement between nodes in a distributed network, despite the possible presence of bugs or malicious agents.
How consensus algorithm works
Basically, a blockchain is a network of nodes connected to each other. For a transaction to be recorded on the blockchain, it needs to be validated simultaneously by all nodes in the network based on a consensus mechanism.
Blockchain has a structure of many blocks linked together, forming a chain. Each block contains information about the hash of the previous block. This hash is generated from the predefined input of the block, including transaction information that has been validated by the nodes.
When a user makes a transaction, the nodes use the blockchain s consensus algorithm (like PoS, PoW, PoA, etc.)…) to validate and record transactions to the new block on blockchain. All nodes must then download information about the newly validated transaction block, in order to ensure the consistency and integrity of data on the network.
The consensus algorithm also ensures that changing the data on blockchain is not possible . If a block is changed, the hash of that block will also change. These hashes will be compared with the data of other blocks to check the correctness and match between the hash of the previous and the following block.
Why does blockchain need a consensus algorithm?
The existence of a consensus mechanism is essential for blockchain for a variety of reasons. Here are two main reasons:
Helps ensure nodes perform their roles properly
Blockchain works on the principle of decentralization, with a global network of nodes rather than having control from one intermediary. So how do we ensure that these nodes can validate transactions correctly, operate the blockchain efficiently and prevent fraud?
That is the task of the consensus mechanism. Nodes must obey the rules of the consensus algorithm in order to perform their task properly. If they do not comply, they can be penalized by the slashing mechanism.
Helping blockchain become Byzantine fault tolerant (BFT)
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) is a concept in computer science that describes the ability of a system to continue to function normally even when some elements in the system fail or are deliberately destructive.
The blockchain uses a consensus mechanism to achieve BFT. This means that even if some nodes fail or attempt to attack the network, the blockchain can still maintain its integrity and function normally.
Popular blockchain consensus algorithms
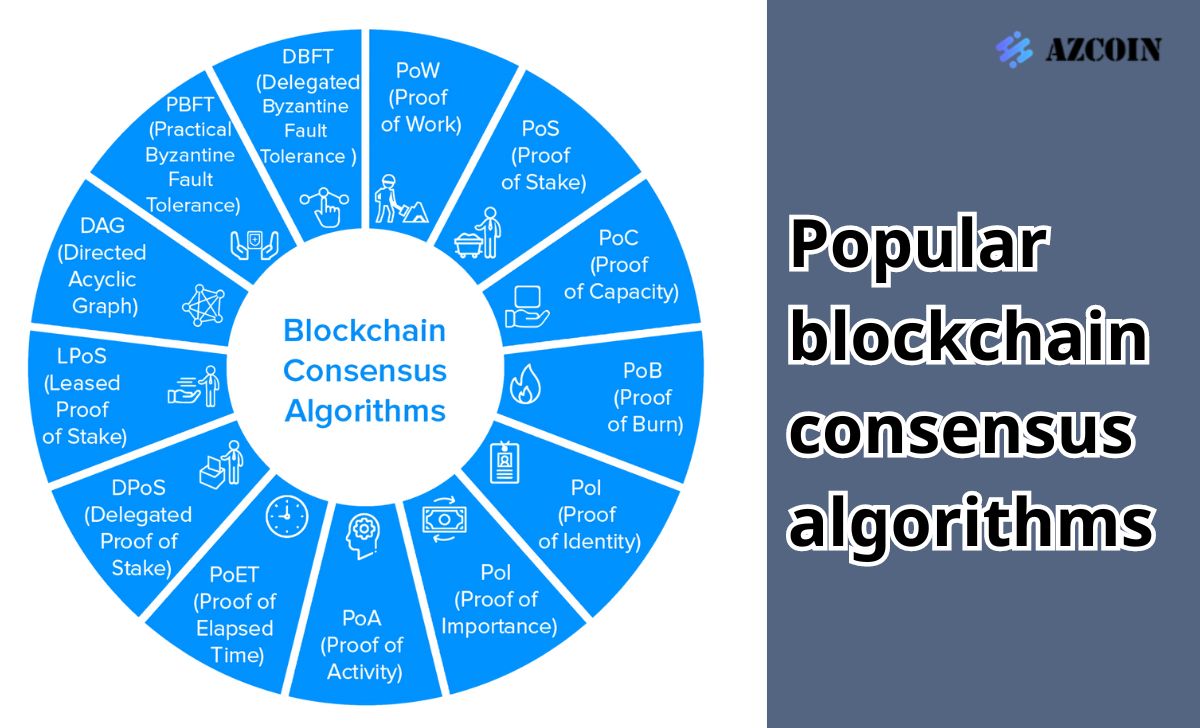
Currently, there are many consensus algorithms used in different blockchain networks. Here are some popular algorithms:
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work (PoW) is one of the first consensus algorithms used in the blockchain, most famously Bitcoin. In PoW, nodes must solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain. The node that solves the first problem is entitled to add a block to the blockchain and receive a reward for blockchain tokens.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus algorithm to PoW, which is used in many blockchains such as Ethereum 2.0. In PoS, nodes must stake a certain number of blockchain tokens to participate in the transaction confirmation process. Nodes that bet more tokens have a higher chance of being selected as validators and receiving rewards.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)

Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a variant of PoS, used in blockchains such as EOS. In DPoS, nodes do not directly validate transactions but instead vote for a group of delegates to do this.
Proof of Authority (PoA)
Proof of Authority (PoA) is an identity-based consensus algorithm, used in blockchains such as VeChain. In PoA, nodes must be verified and allowed to participate in the transaction confirmation process.
Other consensus algorithms
In addition to popular consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), there are many other methods such as Proof of Weight (PoWeight), Proof of Capacity (PoC), Proof of Burn (PoB) and Direct Acyclic Graph Tangle (DAG). To trade cryptocurrencies safely, you can refer to the best cryptocurrency exchanges 2024.
Conclusion
In this article, AZcoin introduces you to the basics of the consensus algorithm and how it works. Understanding this algorithm will not only help you assess the potential of blockchain projects, but also help you make more informed investment decisions!

I am Louis Dang, living in Ottawa, Canada. I am currently working as a trader for AZCoin company, with 7 years of experience in the cryptocurrency market, I hope to bring you useful information and knowledge about virtual currency investment.











