The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a data structure that is being talked about a lot in the field of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional blockchains, DAG uses a completely different approach to storing and validating transactions.
In this article, AZCoin will help you learn in detail about the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) and how it works!
What is Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)?
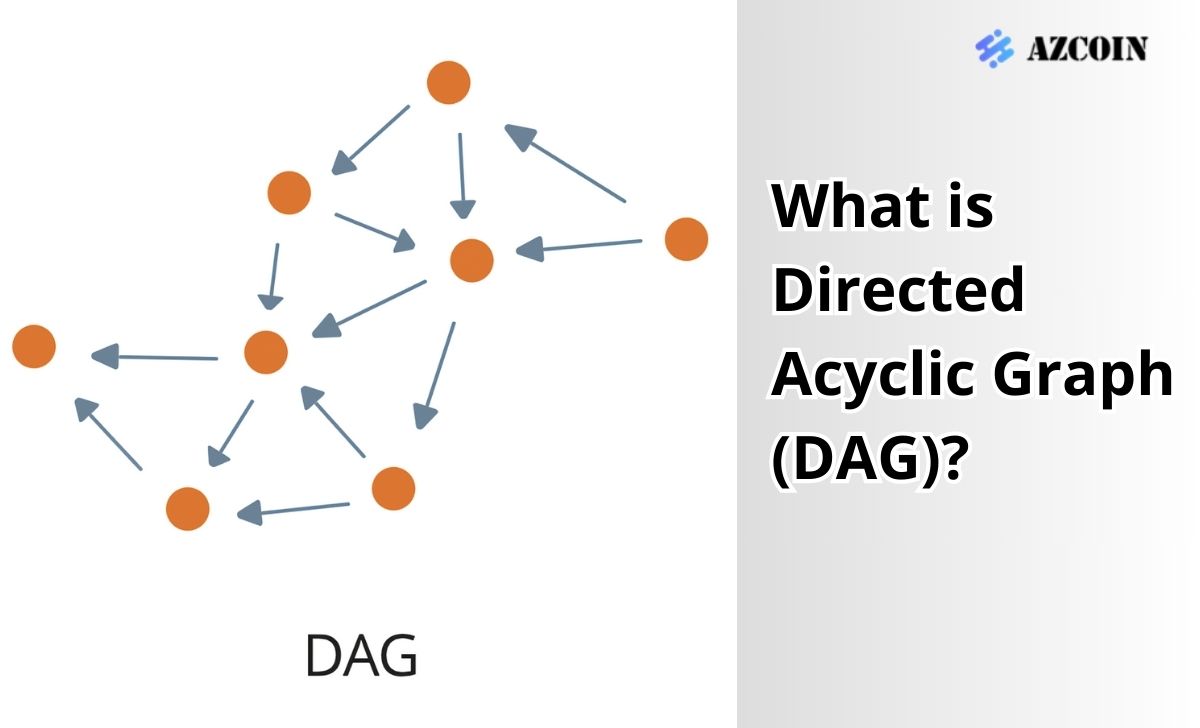
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a type of data structure that allows multiple transactions to be executed simultaneously without waiting for the block mining process as in traditional blockchain systems. In DAG, each transaction is represented as a node and transactions are connected to each other through the verification process, forming a non-cyclic graph structure.
While traditional blockchains supplement data by arranging blocks in order into a linear chain, DAG does not use a chain structure but distributes transactions into a network. This means that validators or miners do not need to compete to find new blocks to add to the chain, which optimizes processing efficiency.
How does Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) work?
As stated above, the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a directional and non-cyclical data structure. In cryptocurrency systems such as IOTA and Nano, DAG is used to store and process transactions.
In this model, each transaction is validated by several previous transactions, called “confirmations.” When a new transaction is introduced into the DAG, it needs to be validated by the previous transactions to ensure validity. Nodes in the network perform the confirmation through a collaborative protocol.
DAG allows for high decentralization and scalability, as there are no restrictions on block size or validation times as in traditional blockchains. It allows for simultaneous transaction processing, minimizing transaction confirmation costs and times.
Applications of DAG in technology
DAG has been successfully applied in many different fields thanks to its ability to optimize transaction and data processing. Some outstanding applications of DAG include:
- IOTA : The application uses a DAG structure called “Tangle” to support zero-fee transactions and massive scalability for the Internet of Things (IoT) . In this system, each new transaction must validate two previous transactions, creating an overlapping transaction network.
- Nano : It uses a structure called Block Lattice to provide fast and fee-free transactions. Each account in the network has a separate blockchain, allowing for simultaneous updates without having to wait for confirmation from the entire network. This helps Nano achieve near-instant transaction speeds.
- Hedera Hashgraph: It uses a unique type of DAG to create a secure and fast decentralized platform. Instead of using PoW (Proof of Work) or PoS (Proof of Stake) consensus, Hedera uses a protocol called gossip-about-gossip and a consensus algorithm called Virtual Voting.
- Constellation: This protocol uses DAG to provide scalability and security for big data. It is specifically designed to support distributed systems that require processing large amounts of data in real time.
Advantages and disadvantages of Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)

Advantages
- High Scalability : Because there is no need to wait for blocks to be created, DAG allows for the processing of multiple transactions simultaneously, improving scalability.
- Fast transaction speed : Transactions can be confirmed instantly thanks to the non-cyclical structure and parallel processing capabilities.
- Reduced transaction fees : Many systems that use DAG, like IOTA and Nano, offer the ability to make transactions for free or at very low fees.
- Decentralization: DAG supports network distribution without relying on central nodes to make transactions and store data.
- High Availability: Thanks to the distributed architecture and scalability of DAG, the network maintains good performance even when some nodes are interrupted.
Disadvantages
- High complexity : The structure and implementation of DAG is more complex than traditional blockchain, requiring more effort and costs to develop and maintain.
- Consensus issues : Ensuring consensus in DAG systems can be more complex, requiring advanced algorithms and technical solutions to ensure consistency and security.
- 51% chance of being attacked: DAG networks are also vulnerable to 51% attacks, when one entity controls more than half of the network’s computing power, which can generate fake transactions.
- Difficulty in validating transactions: In the DAG system, transactions are not confirmed through integration into a block as in the blockchain, which makes the process of validating transactions more complicated.
- The possibility of an error: Since DAG does not have a uniform structure like blockchain, any node in the network can create an invalid transaction, affecting the integrity of the system.
Comparison between DAG and Blockchain
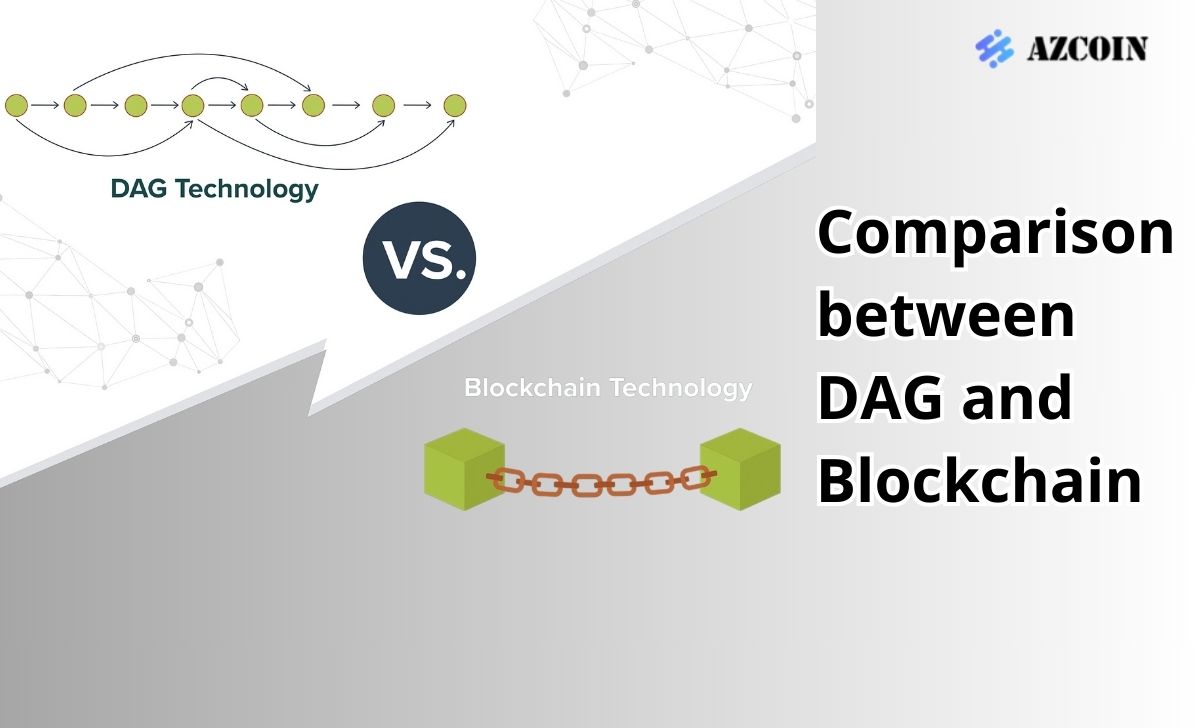
| Factor | DAG | Blockchain |
| Structure | No blocks, transactions organized as a directed graph | Data stored in sequential blocks |
| Scalability | High, allows parallel processing | Limited by block size and creation time |
| Speed | Fast, transactions are confirmed instantly | Slower, requires time for block confirmation |
| Transaction Fees | Low or no fees | Usually fees for each transaction |
| Complexity | More complex to implement and maintain | Simpler, easier to understand and implement |
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) and Blockchain both have their own advantages and limitations, and the choice between them depends on the specific goals and requirements of each application.
Conclusion
Just now is the detailed information about Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) that AZcoin has just introduced to you. Hope this article will help you better understand DAG and can apply it to the latest research projects offline!

I am Louis Dang, living in Ottawa, Canada. I am currently working as a trader for AZCoin company, with 7 years of experience in the cryptocurrency market, I hope to bring you useful information and knowledge about virtual currency investment.











