Peer-to-peer (P2P) is a model that many people are interested in because it allows nodes to connect directly and exchange data without the need for a central server. So what are the main benefits of the P2P model?
Follow the AZCoin article to discover five outstanding benefits of this model.
What is Peer-to-peer (P2P)?

Peer-to-peer (P2P) is a network model in which devices or nodes (peers) in the network can communicate and exchange data directly with each other without going through an intermediate server. In this model, each node can be both a sender and a receiver of data and can also provide services to other nodes in the network.
How Peer-to-peer work
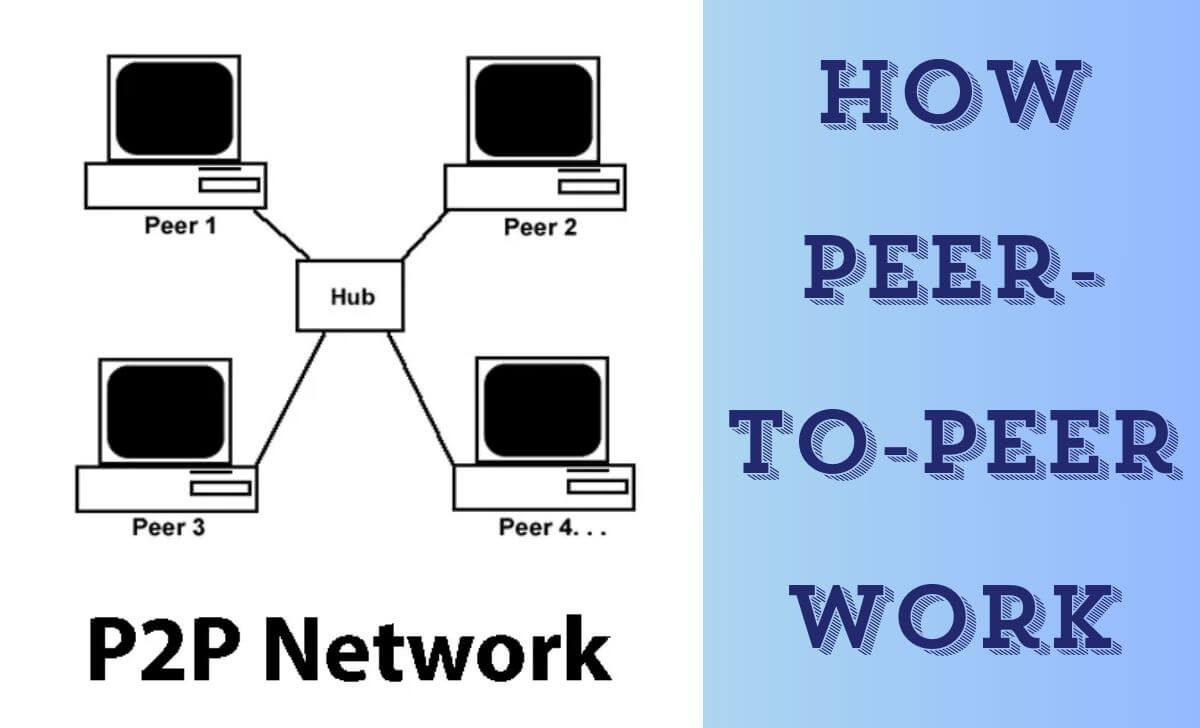
The P2P model works by having devices connect directly to each other to share resources without going through a central server. Instead, each device participating in the network acts as both a server, providing resources, and a client, accessing resources from other devices.
When a user wants to access a file on a P2P network, they send a request to the network. Other devices, including those using technologies like IOTA, will search for that file in their storage and send back the search results. When the file is found, it will be transferred directly from the device storing it to the requesting device, through a series of connections between intermediate devices. This creates a distributed, flexible, and highly fault-tolerant network.
P2P network classification
Below are the three main types of P2P networks:
Unstructured P2P networks
Unstructured P2P networks are models where nodes connect randomly without any specific organization. Searching for data relies on broadcasting requests to all nodes, similar to how IoT (Internet of Things) devices might broadcast data requests.
In BitTorrent, files are shared without any structure for managing the data. Although easy to deploy and scale, searching for data can be inefficient and doesn’t guarantee the presence of data.
Structured P2P networks
Structured P2P networks organize nodes and data according to certain rules, making searching and storing data more efficient. Chord, a DHT system, is a typical example, providing structure and fast searching capabilities. However, deployment and management can be more complex than unstructured networks.
Hybrid P2P networks
Hybrid P2P networks combine elements of both unstructured and structured networks, such as BitTorrent combining file sharing with DHT for data searching. This model provides greater flexibility and search efficiency but requires more complex management and deployment.
5 advantages of the P2P model

The P2P model offers many outstanding benefits, including:
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a distributed network, increasing transparency and reducing the risk of fraud. This is crucial for platforms like AZcoin – best crypto exchange 2024 – where transparency builds user trust.
- Low cost: Eliminating the need for a central server reduces the cost of operating and maintaining the network. Nodes in a P2P network share resources, reducing the financial burden on service providers.
- High reliability: P2P networks are generally more reliable because data is widely distributed. Even if some nodes fail, the network can continue to operate thanks to the remaining nodes.
- Scalability: Peer-to-peer networks are highly scalable because as more nodes are added to the network, resources and bandwidth are also distributed more widely, improving the performance and data processing capabilities of the network without changing the central structure.
- Flexibility: The P2P model allows nodes in the network to share and manage resources flexibly. This supports a wide variety of applications, from file sharing and cryptocurrency transactions to communication and collaboration systems.
Disadvantages of the Peer-to-peer model
While the Peer-to-peer model offers many benefits, it also has some notable disadvantages, such as:
- Security: P2P networks can have security issues because the nodes in the network are often not centrally managed and may lack control. This increases the risk of cyberattacks, malware and intrusions from untrusted nodes.
- Manageability: Managing and maintaining a P2P network can be difficult due to its distributed nature. Synchronizing data between nodes and ensuring that all nodes are functioning properly can become complex.
- Search performance: Unstructured Peer-to-peer networks can have difficulty searching for data quickly and efficiently. Broadcasting search requests to all nodes or a large portion of nodes can reduce search performance and speed.
- Tuning capability: Peer-to-peer networks may not be able to optimize the distribution of resources and data. As the number of nodes increases, resource management and distribution can become more complex and can lead to congestion or uneven distribution.
- Synchronization: Synchronization of data between nodes in a P2P network can be difficult, especially when there are many nodes and data needs to be updated frequently. This can lead to inconsistencies in information and reduce network efficiency.
Applications of P2P networks in blockchain
Below are some prominent applications of P2P networks in Blockchain:
- Cryptocurrency transactions: Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains use P2P networks to confirm transactions and update the ledger. Users can exchange cryptocurrencies directly with each other without going through banks or intermediaries. This not only saves time but also reduces transaction costs.
- Transaction validation: Transactions on the blockchain are validated via a P2P network, where miners verify and agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain.
- Data storage: In blockchains like IPFS, Peer-to-peer networks are used to store and share distributed data. Data is fragmented and stored across multiple nodes in the network, improving accessibility and reducing the risk of data loss.
- Smart contracts: Smart contracts on the blockchain operate on a P2P network, where the terms and conditions of the contract are automatically and consensually executed by nodes in the network, without the need for third-party intervention.
- DeFi ecosystem: In DeFi applications, Peer-to-peer networks support asset trading, lending and liquidity provision without the need for traditional financial intermediaries. Transactions and contracts are executed directly between participating parties over the P2P network.
- Identity management: Decentralized identity management systems use P2P networks to verify and manage user identities. This enhances privacy and security of personal data, allowing users to more effectively control their information.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article has helped you better understand how Peer-to-peer can optimize data and resource sharing in distributed networks. To continue learning and receiving more updates on technology and new trends, contact AZcoin for further support and advice.

I’m Jessi Lee, currently living in Singapore. I am currently working as a trader for AZCoin company, with 5 years of experience in the cryptocurrency market, I hope to bring you useful information and knowledge about virtual currency investment.
Email: [email protected]











